Why is GNSSRO Data Important?
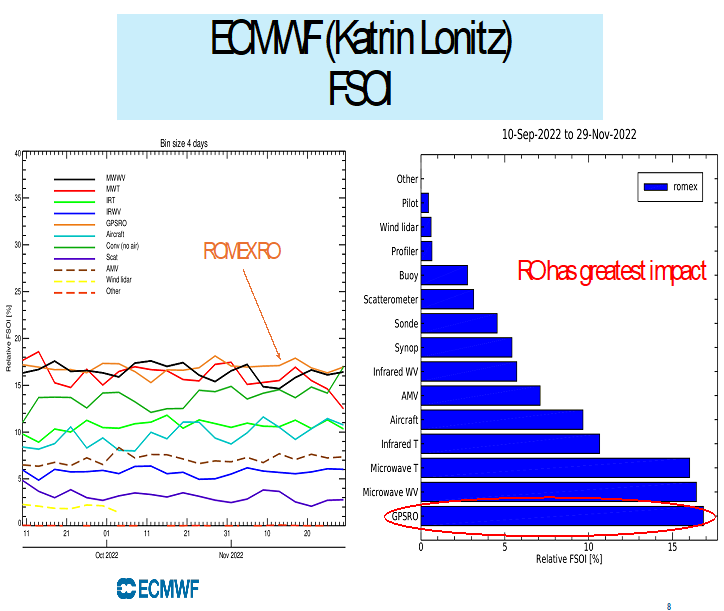
Figure 1. The reduction of forecast error using various observations (left panel) and the relative FSOI (%) (right panel). RO has the largest impact on reducing forecast errors among all data.
RO data provides valuable and unique atmospheric information because of their high accuracy and precision, vertical resolution, insensitivity to clouds and precipitation, and global coverage (see Ho et al., 2019) . With a high vertical resolution of between 200 and 600 m, RO temperature profiles can resolve delicate atmospheric structures, which is impossible for MW/IR nadir viewing sounders. RO is the only self-calibrated satellite remote sensing technique whose raw measurements can be traced to the International System of Units of Time. RO measurements are well suited for climate monitoring because they (i) have no significant mission-dependent biases above 5 km, (ii) are of high precision and accuracy, and (iii) are minimally affected by clouds and precipitation. Thus, RO data can serve as benchmark datasets to study atmospheric variability.
With 12K occultation profiles per day, GNSS RO data ranked 4th most impactful data set for reducing forecast errors. With more than 12K occultation profiles (40K RO profiles) per day, ECMWF demonstrated that GNSS RO ranked the 1st most impactful data sets (among IASI, AMSU, radiosondes, aircraft radio sound, etc) for reducing the forecast errors (see Figure 1).
Reference: Ho, S.-P., and co-aithors, 2019: The COSMIC/FORMOSAT-3 Radio Occultation Mission after 12 years: Accomplishments, Remaining Challenges, and Potential Impacts of COSMIC-2, Bul. Amer. Meteor. Sci., DOI: 10.1175/BAMS-D-18-0290.1.
